문제
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2178
2178번: 미로 탐색
첫째 줄에 두 정수 N, M(2 ≤ N, M ≤ 100)이 주어진다. 다음 N개의 줄에는 M개의 정수로 미로가 주어진다. 각각의 수들은 붙어서 입력으로 주어진다.
www.acmicpc.net
접근
1. DFS -> time over
2. BFS
풀이
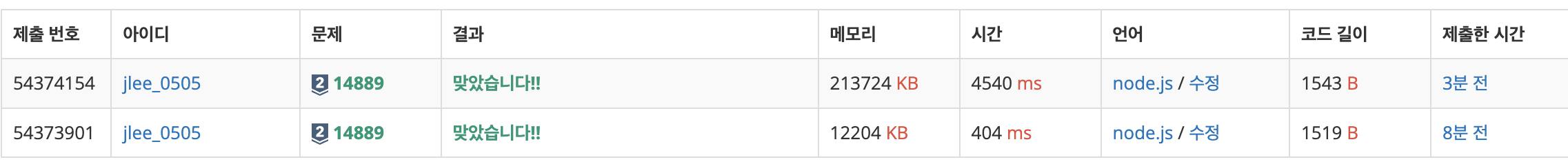
take-1: 실패 (10)
- [0,3] 큐를 마지막으로 반복문이 멈췄다.
- idxPairs 까지는 뽑히는데 validPairs 에서 아무것도 검출되지 않았다. -> nx, ny 범위조건을 둘다 N 으로 해놨었다.
const solution = (input) => {
const [N, M] = input.shift().split(" ").map(Number);
const graph = [...input].map((v) => v.split("").map(Number));
let answer = Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER;
const inValidRange = (pair) => {
const [nx, ny] = pair;
if (nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= N || ny >= N) return false;
else if (graph[nx][ny] === 1) return true;
return false;
};
const bfs = (row, col) => {
const queue = [[row, col]];
const seen = new Array(N).fill(0).map(() => new Array(N).fill(false));
seen[row][col] = true;
let cnt = 1;
while (queue.length) {
const [x, y] = queue.shift();
graph[x][y] = 0;
const idxPairs = [
[x - 1, y],
[x, y + 1],
[x + 1, y],
[x, y + 1],
];
const validIdxPairs = idxPairs.filter((v) => inValidRange(v));
for (let idxPair of validIdxPairs) {
const [nx, ny] = idxPair;
if (graph[nx][ny] === 1 && !seen[nx][ny]) {
seen[nx][ny] = true;
cnt++;
console.log("nx,ny: ", nx, ny, "\n", "cnt: ", cnt, "queue: ", queue);
queue.push([nx, ny]);
}
}
}
return cnt;
};
const count = bfs(0, 0);
answer = answer < count ? count : answer;
return answer;
};
console.log(solution(input));take - 2: fail (17)
const solution = (input) => {
const [N, M] = input.shift().split(" ").map(Number);
const graph = [...input].map((v) => v.split("").map(Number));
let answer = Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER;
const inValidRange = (pair) => {
const [nx, ny] = pair;
if (nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= N || ny >= M) return false;
if (graph[nx][ny] === 1) return true;
return false;
};
const bfs = (row, col) => {
const queue = [[row, col]];
const seen = new Array(N).fill(0).map(() => new Array(M).fill(false));
seen[row][col] = true;
let cnt = 1;
while (queue.length) {
const [x, y] = queue.shift();
graph[x][y] = 0;
const idxPairs = [
[x - 1, y],
[x, y - 1],
[x + 1, y],
[x, y + 1],
];
const validIdxPairs = idxPairs.filter((v) => inValidRange(v));
console.log(x, y);
console.log(idxPairs);
console.log(validIdxPairs);
for (let idxPair of validIdxPairs) {
const [nx, ny] = idxPair;
if (graph[nx][ny] === 1 && !seen[nx][ny]) {
seen[nx][ny] = true;
cnt++;
queue.push([nx, ny]);
}
}
console.log("queue: ", queue);
}
return cnt;
};
const count = bfs(0, 0);
answer = answer < count ? count : answer;
return answer;
};
console.log(solution(input));
tial-3: success!!
const solution = (input) => {
const [N, M] = input.shift().split(" ").map(Number);
const graph = [...input].map((v) => v.split("").map(Number));
let answer = Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER;
const inValidRange = (pair) => {
const [nx, ny] = pair;
if (nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= N || ny >= M) return false;
if (graph[nx][ny] === 1) return true;
return false;
};
const bfs = (row, col) => {
const queue = [[row, col]];
const seen = new Array(N).fill(0).map(() => new Array(M).fill(0));
seen[row][col] = 1;
while (queue.length) {
const [x, y] = queue.shift();
graph[x][y] = 0;
const idxPairs = [
[x - 1, y],
[x, y - 1],
[x + 1, y],
[x, y + 1],
];
const validIdxPairs = idxPairs.filter((v) => inValidRange(v));
console.log(x, y);
console.log(idxPairs);
console.log(validIdxPairs);
for (let idxPair of validIdxPairs) {
const [nx, ny] = idxPair;
if (graph[nx][ny] === 1 && !seen[nx][ny]) {
seen[nx][ny] = seen[x][y] + 1;
queue.push([nx, ny]);
}
}
console.log("queue: ", queue);
}
return seen[N - 1][M - 1];
};
const count = bfs(0, 0);
answer = answer < count ? count : answer;
return answer;
};
console.log(solution(input));'Board > 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 14502 연구소 (JavaScript, Node.js) (0) | 2023.01.31 |
|---|---|
| 백준 10828 자바스크립트 (0) | 2023.01.31 |
| 백준 2667 단지 찾기 자바스크립트 (0) | 2023.01.27 |
| 백준 2606 자바스크립트 (0) | 2023.01.26 |
| 백준 2468 자바스크립트 (0) | 2023.01.25 |